Considered a pest by some, and a terrifying nightmare to others, there is little escaping insects during the summer season. Fear of getting stung by a bee, wasp, fire ant, or hornet can cause even the toughest men and women to start flailing wildly at the very sight of one of these pesky pests.
While getting stung or bitten does hurt, very rarely does an insect sting cause an allergic reaction that necessitates seeking medical assistance. Only approximately three percent of Americans suffer from a stinging insect allergy. However, many people never realize they possess an allergy to insect stings until it’s too late. Knowing the difference between a normal reaction and a serious allergic reaction to an insect sting can help save you money on costly emergency room visits and help put your mind at easy when heading outdoors.
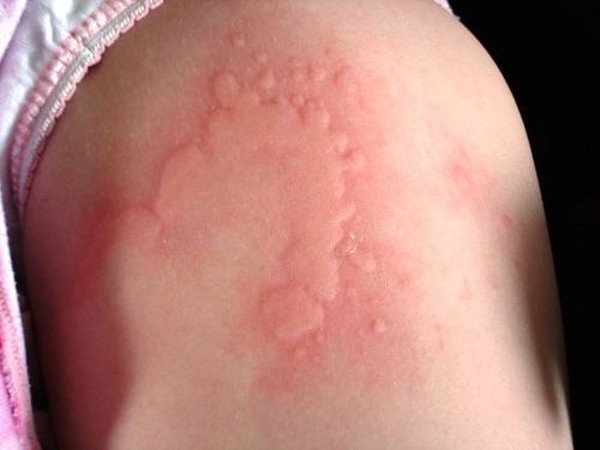
Types of Reactions
While the severity of how someone reacts to an insect sting will vary, there are three general types of reactions:
- Normal- A normal and healthy reaction to an insect sting results in pain, swelling, and redness around the affected area.
- Localized- A localized reaction causes swelling to occur in to an area that extends beyond the site of the sting. A person stung on the wrist, for example, may experience swelling of the hand or even possibly the entire arm. This can certainly seem startling and a cause for alarm, however, these types of stings, no matter how disturbing in appearance, don’t pose any more of a danger to your health than a normal reaction.
- Allergic-By far the most serious type, an allergic reaction to an insect sting can have serious long-term health consequences, and requires you to seek immediate medical attention.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to insect stings can cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening type of reaction that occurs rapidly, and may include some of the following symptoms:
- Trouble breathing
- Itchy, red hives that spread beyond the area around the sting
- Swelling of the face, throat, or mouth
- Trouble swallowing
- Wheezing
- Onset of anxiety and an inability to relax
- Accelerated heart rate
- Dizziness
- A sharp drop in blood pressure
Again these symptoms are very rare, as less than 50 deaths a year are attributed to anaphylaxis shock resulting from an insect sting. However, these reactions can occur in less than 10 minutes after being stung, and can lead to cardiac arrest, shock, and unconsciousness.
While caution never hurts in a situation where you suspect your health is in danger, keep in mind you could be experiencing a mild allergic reaction if you develop any of the following symptoms:
- Pain and redness in the area around the sting
- Mild to moderate swelling
- A flushed feeling at the area of the sting
- Itching
If you develop symptoms consistent with a mild allergic reaction, you need to take care to avoid being stung again during the summer season. Individuals who suffer an allergic reaction after an insect sting have a 60 percent chance of suffering a more severe reaction if stung again.
Allergic reactions are generally treated with epinephrine (adrenaline), which can be self-administered or by a doctor, time permitted, after being stung. If you suffer from a severe allergic reaction to insect stings, talk with your doctor about acquiring an epinephrine sting kit. While the use of these kit can help save your life, they should not be used as a substitute for medical attention. You should immediately contact your doctor after using the kit, or seek medical attention at a local hospital or clinic.
Timothy Lemke blogs about health for Dr. Melissa Beadnell, a dentist in Hillsdale Portland at Beadnell Family Dentistry.