Not everyone can enjoy milk from their birth. The alarming rise in dairy related allergies or intolerance is something that has left scientists and health experts bewildered. In the past, cases of such allergies were rare but today, infants face the greatest risk in developing milk allergies.
Those who can’t have milk tend to experience very unpleasant sensations or symptoms soon after taking in any kind of dairy product. These can range from simple vomiting to severe abdominal cramping or even hives and itchy skin condition like eczema. When you experience an adverse reaction after ingesting milk, the first thing to ascertain is whether it is due to milk allergy or lactose intolerance. Usually, people confuse the two to be synonyms but the truth is that they are completely different afflictions of the human body.
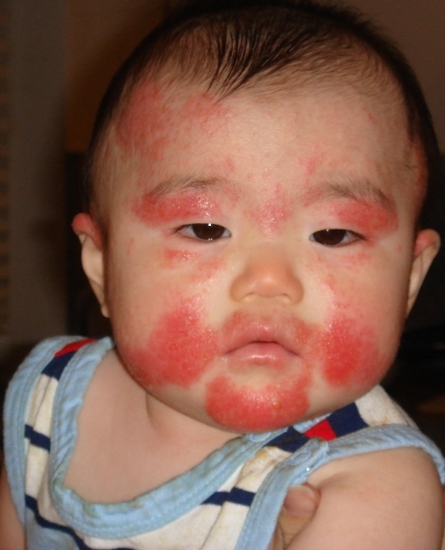
Milk Allergy
The immune system is in charge of fighting off foreign bodies within the system. When it turns against harmless bodies targeting and destroying them, it causes allergic reactions. This condition is also called hypersensitivity. Hence, when a person takes in milk, the immune system in an allergic body shall go into overdrive and try to eradicate milk proteins from the body. This is called milk allergy and it is related to proteins present in milk. The body digests milk and gets nutrients from it but it also undergoes an allergenic reaction in the process releasing high levels of histamine into the body causing inflammation and other symptoms as previously mentioned.
Some direct indications of an allergic reaction to dairy products include dark circles around the eyes, vomiting, hives, wheezing, eczema, cramping and sneezing. Children may show decreased concentration, hyperactivity or red ear lobes. In very rare situations, the allergic reaction manifests as an extreme full body condition also called anaphylaxis. This severe condition constricts the nasal passage, makes it hard for the person to breathe, speak, and increases blood pressure and heart rate. Untreated, it can be fatal.
Lactose Intolerance
In food intolerance, the immune system remains intact and does not go crazy. Histamine is not released and so inflammation related symptoms never develop. Dairy products contain a natural sugar called lactose that can only be metabolized into glucose by an enzyme secreted from the outer lining of the small intestine called lactase. However, some folks naturally produce limited amounts of lactase because of which lactose remains undigested in the intestine leading to many abdominal symptoms.
The symptoms associated with lactose intolerance include diarrhea, gas, bloating, abdominal cramping, nausea, and gurgling sounds. These symptoms can take up to 2 hours to appear making it hard to diagnose the condition. In rapid appearance, it can be anywhere between 10 to 30 minutes.
Regardless of whether you have lactose intolerance or milk allergy, the only way to prevent it is to stop taking in anything that even remotely uses dairy products. In case you suffer from an acute allergic reaction, it is best to carry around a vial of epinephrine so as to relax the air passage during anaphylaxis shock. Even in moderate reactions, it’s best to visit a doctor and ascertain the situation.
Sandra Jackson is really passionate about milk allergy (in Denmark, where she lives, people refer to this term as Mælkeallergi) and enjoys sharing her knowledge in various blogs online.